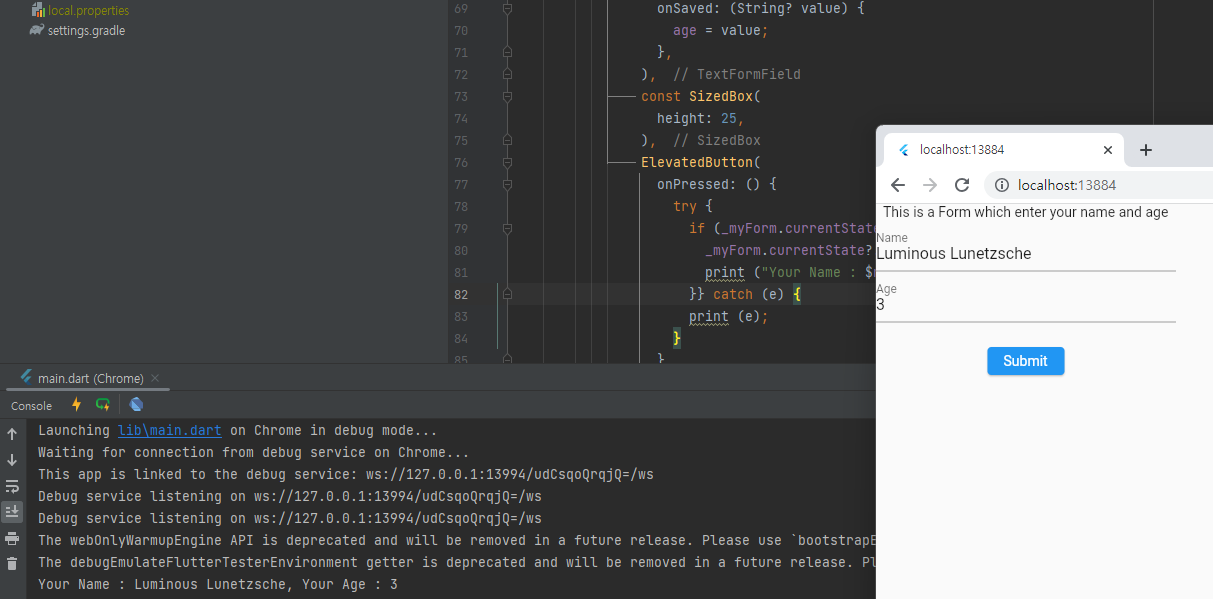
Form은 텍스트 필드처럼 복잡하지 않으며, 우리가 넣은 값을 간단히 검증하고 전달받을 수 있다.
https://github.com/shechren/DIM/tree/master/do7
전체 코드는 여기에 있다.
1
2
3
final _myForm = GlobalKey<FormState>();
String? name;
String? age;
final _myForm으로 FormState를 가져와 선언한다.
name과 age는 처음에는 null 값이니 ?로 선언한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
child: Column(
children: [
const Text("This is a Form which enter your name and age"),
Form(
key: _myForm,
child: Column(
children: [
TextFormField(
decoration: const InputDecoration(
labelText: "Name",
),
validator: (value) {
if (value?.isEmpty ?? false) {
return "Please enter your Name";
}
return null;
},
onSaved: (String? value) {
name = value;
},
),
TextFormField(
decoration: const InputDecoration(
labelText: "Age",
),
validator: (value) {
if (value?.isEmpty ?? false) {
return "Please enter your Age";
}
return null;
},
onSaved: (String? value) {
age = value;
},
),
const SizedBox(
height: 25,
),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {
try {
if (_myForm.currentState?.validate() ?? false) {
_myForm.currentState?.save();
print ("Your Name : $name, Your Age : $age");
}} catch (e) {
print (e);
}
},
child: const Text("Submit"),
)
],
)
)
]
)
컬럼의 첫번째로 텍스트를 넣는다.
그리고 폼을 넣는데, 폼에는 키와 차일드가 필요하다. 키는 아까 우리가 만든 final로 선언한 _myForm을 넣고, child에는 폼의 구성 요소인 TextFormField를 넣는다.
TextFormField는 validator 함수를 요구하는데, 여기에 들어가는 매개변수가 바로 우리가 입력한 String 값이다.
따라서 우리는 이 매개변수를 if문으로 검사할 수 있다. 위에서는 onSaved 메소드를 호출해서 해당 값을 변수에 대입했다.
마지막으로 ElevatedButton을 호출한다. 여기서는 name과 age의 값이 모두 있다면 그것을 저장하거나 라우트로 보내거나 출력을 한다. 여기서는 출력을 했다.